Lipedema and Nutrition
Avinav
July 25, 2023
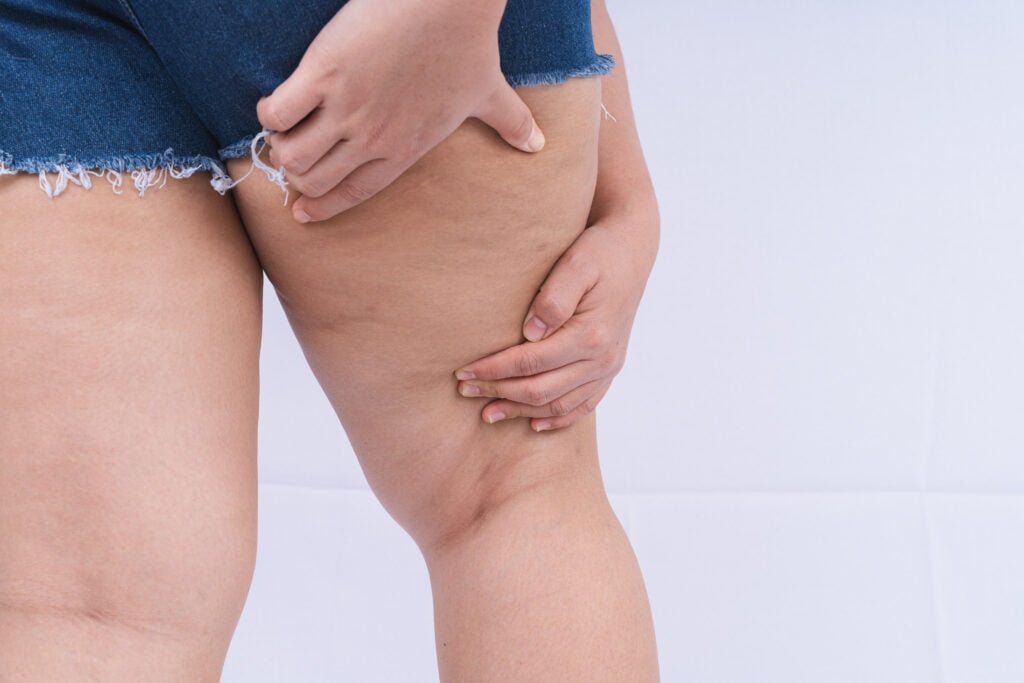
Millions of individuals worldwide, mostly women, suffer from the medical ailment known as lipedema. It is frequently misdiagnosed or ignored because of how it resembles lymphedema and obesity. Lipedema, on the other hand, must be distinguished as a unique condition marked by abnormal fat deposition in the lower extremities, usually the legs and occasionally the arms. Although the precise origin of lipedema is still unknown, mounting evidence points to a connection between nutrition and the condition’s development. This blog will explain how to control lipedema through dietary and lifestyle modifications and examine the connection between lipedema and nutrition.
Knowing lipedema
A chronic and progressive disease called lipedema is characterised by an abnormal buildup of adipose tissue in particular bodily parts. Also known as “a syndrome characterized by fat legs and orthostatic edema” It is challenging for persons who have this excess fat to lose weight because, unlike regular fat, it does not respond well to diet and exercise. A symmetrical rise in fat around the hips, thighs, and buttocks is a common early sign of the illness, which then gradually spreads downward. Lipedema can have a considerable negative influence on a person’s quality of life when it progresses to the point that there is discomfort, swelling, and trouble moving.
Function of nutrition in Lipedema
Nutrition can aggravate the condition and have an impact on how lipedema develops, even though genetics play a key role in this process. Here are a few crucial ones:
Foods that cause inflammation: Consuming foods that cause inflammation can cause lipedema, which is characterized by chronic inflammation. These could include refined carbs, sugary snacks, processed foods, and harmful fats. Symptoms can be reduced by eating an anti-inflammatory diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
Fluid Retention: Swelling and fluid retention are common in people with lipedema. Since excessive sodium consumption promotes to water retention, cutting back on salt consumption can help maintain fluid balance.
Imbalances in the hormones can affect how the body stores and distributes fat. The growth of lipedema in women may be impacted by hormonal changes over various life stages, such as pregnancy, menopause, or hormonal treatments. A healthy diet can control hormones and reduce any negative effects.
Weight Control: Although lipedema fat is resistant to traditional weight loss techniques, keeping a healthy weight is essential to properly treat symptoms. Balanced meals that are high in nutrients can promote overall health and wellbeing.
Gut health: Recent studies point to a link between good gut health and a number of metabolic disorders, including lipedema. Probiotics and fiber-rich meals might help to maintain a healthy gut flora, which may reduce the symptoms of lipedema.
Function of Nutrition
- Have control on weight
- Improvise gut health
- Reduce foods causing inflammation
Nutritional Advice
- Keep yourself hydrated
- Reduce salt consumption
- Emphasize on eating whole foods
Nutritional Advice for the Treatment of Lipedema
Emphasis on Whole Foods: Place a strong emphasis on consuming a diet full of unprocessed, whole foods such fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. While lowering inflammation, these meals offer vital nutrients.
Adequate Hydration: Staying adequately hydrated lowers water retention and enhances lymphatic circulation in general. Make an effort to hydrate yourself well throughout the day.
Practice mindful eating by paying attention to your hunger and fullness indicators. This can encourage the consumption of healthier foods and help prevent overeating.
Reduce Consumption of Inflammatory Foods: Cut back on the intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and bad fats. Choose anti-inflammatory foods instead, such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Reduce your salt consumption to control fluid retention and reduce edema in the affected areas.
Avoid Crash Diets: Following crash diets or drastically cutting caloric intake might cause nutrient deficiencies and worsen lipedema symptoms. Instead, concentrate on making long-term, sustainable lifestyle improvements.
Conclusion
Although lipedema cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed via dietary and lifestyle adjustments, which can greatly reduce its symptoms and enhance general health. People with lipedema can improve their quality of life and better control the condition’s progression by adopting a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet and making thoughtful decisions. To develop a customized nutrition plan catered to every person’s needs and circumstances, always seek the advice of a medical practitioner or certified dietitian.
To connect with us click on the button below
To know more fill in the details below:
Recent Posts
Have Any Question?
Lipedema is a condition that causes excess fat to accumulate in the lower part of the body.
- +919515106591
- srinageshlipedema@gmail.com



